Research & Development
Posted on
October 17, 2021
in
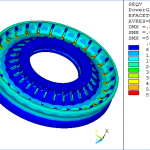
Advancement In Torsional Damper
New Trends in Automotive Engines
- Emission regulation compliance.
- Reduction in fuel consumption and CO2 emissions.
- EGR
- After treatment systems.
- Engine downsizing
- More power from smaller engines.
- Flat torque curve for almost 70% of engine speed.
- Cylinder cutoff or deactivation.
- Cylinder fuel cut off at partial load or idle condition.
- Reducing number of cylinders.
- Engine over speeding conditions.
- Low Density
- Better heat transfer coefficient than casting
- Mechanical properties at par with S.G. Iron
- Reduction in wastage in the manufacturing process
Advance Material
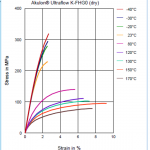
- High Heat stability upto 200°C.
- Higher tear resistance.
- Excellent resistance to oil, coolant, fuels and hydrocarbons.
- Better damping properties.
- High elasticity.
- Lower compression set.

Advance Material 1
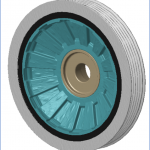
Fin Design
- Fins are passive heat exchangers.
- Better convective heat transfer coefficient.
- Better conductive heat transfer coefficient.
- Higher under hood and operating temperatures.
- Airflow direction.
- As cast fins on damper housing.
Advance Damping Material
- Change in viscosity is lower at higher shear rate.
- High Heat stability upto 140°C.
- High Shear Stability.
- Retaining damper functionality over lifetime.

- Rapid change in rheological characteristics.
- High damping can be achieved in lower envelope size
- High heat stability
- Limitations